Neuroscientific Methods
(f)MRI - Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
(Functional) magnetic resonance imaging is used to measure brain activity as well as structural changes of the brain. This method can be used to measure brain activity also in deep structures of the brain. This method is one of the most advanced to investigate the neuroscience of behavior in humans.
NIRS - Near Infrared Spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a tool to measure brain activity on the surface of the cortex using infrared light. This method has the advantage to be easy to use.
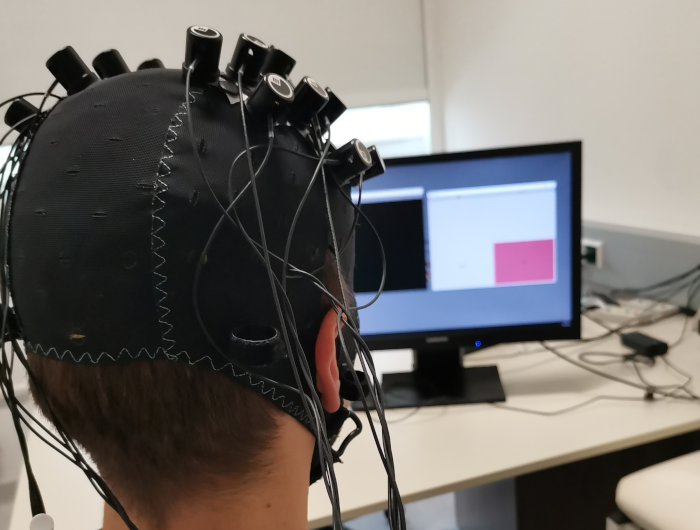
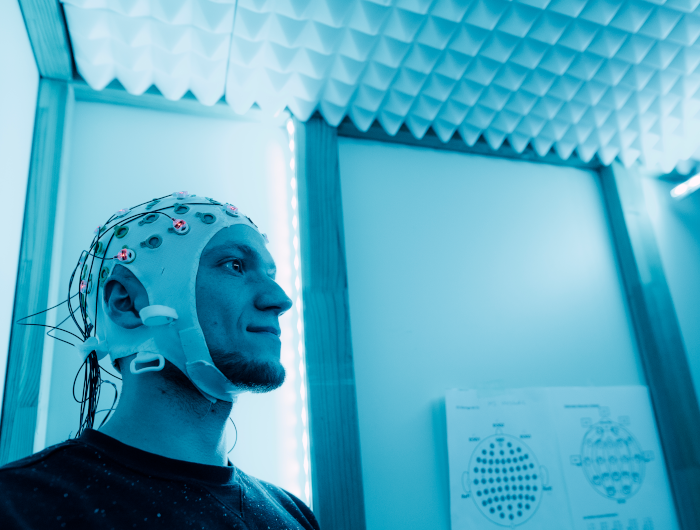


EEG - Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) measures the electrical brain activity. Electrodes are used to measure the electrical activity from the surface of the scalp. The biggest advantages of this specific methods lies in its high temporal resolution.
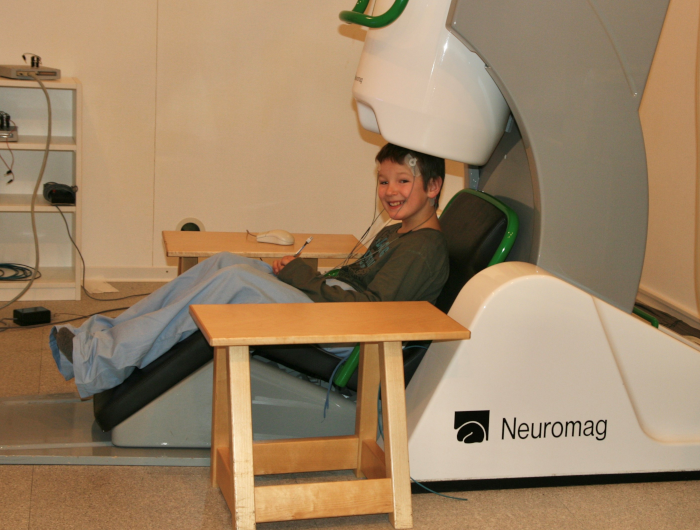
MEG - Magnetoencephalography
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) allows the contact-free measurement of magnetic fields over the head surface. These fields penetrate different tissue layers without distortion and enable a precise localization of cortical sources. Fig.: 122- channel whole head system at the Neurological University Clinic Heidelberg (research cooperation).
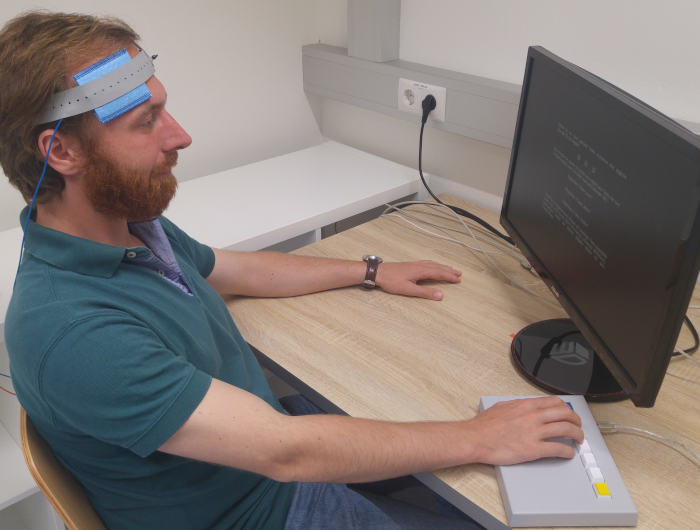

TMS/tES - Transcranial Magnetic/Electrical Stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcranial electrical stimulation (tES) are non-invasive methods of brain stimulation which modulate the activity of brain areas and neuronal networks. They allow studying causal effects of brain activity on psychological processes. TMS is based on the induction of very short-time (<1ms) electrical current to the brain by an electromagnetic field, whereas tES is based on the direct application of a very small electrical current (~1mA) via electrodes on the surface of the head. Both methods are able to induce inhibiting or activating effects.
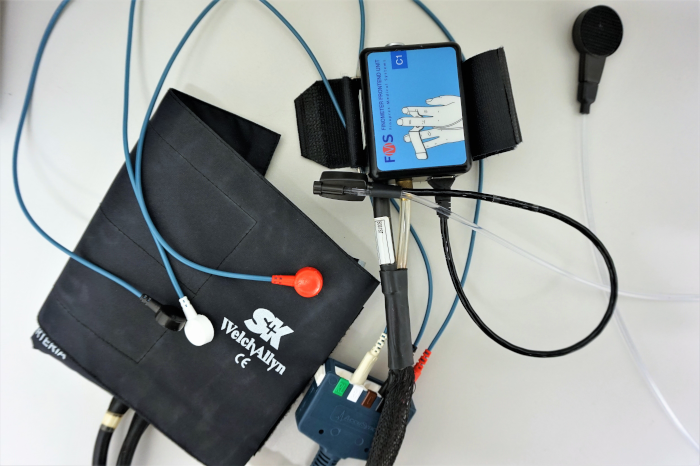
Psychophysiological Measurements
The analysis of the autonomic nervous system and the neuroendocrine system enables insights into stress- and regeneration progress (tonic parameters) as well as into cognitive and affective processes (phasic parameters). Typical psychophysiological variables include: skin conductance, skin temperature, heart rate and hear rate variability, blood pressure, cardiac output, peripheral resistance and intima media thickness. Neuroendocrine variables like cortisol, adrenaline, noradrenalin and serotonin are determined by salvia, blood or urine analysis. Psychophysiological measures have the advantage to be applicable in the laboratory as well as under realistic circumstances in the field (ambulatory psychophysiological assessment).
